 |
| Photo credit:electrical technology |
Hydropower or hydro energy is one of the oldest and largest sources of renewable energy, which uses the natural flow of moving water to generate electricity. In 2020, hydropower plants produced about 7.3% of total U.S. electricity generation and about 37% of electricity generation from renewable energy. It is a clean and sustainable form of energy that does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions, making it an attractive option for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Hydroelectricity is generated by either damming or diverting a body of water to harness the power of its movement. The water is then released through turbines, which spin a generator to produce electricity. Unlike other sources of renewable energy, such as solar and wind, hydropower is not dependent on weather conditions and can provide a constant and reliable source of energy. Additionally, hydropower plants can be built in a range of sizes, from large-scale facilities to small-scale micro hydropower systems, making it a flexible option for a variety of energy needs.
Understanding HydroPower
Definition of HydroPower
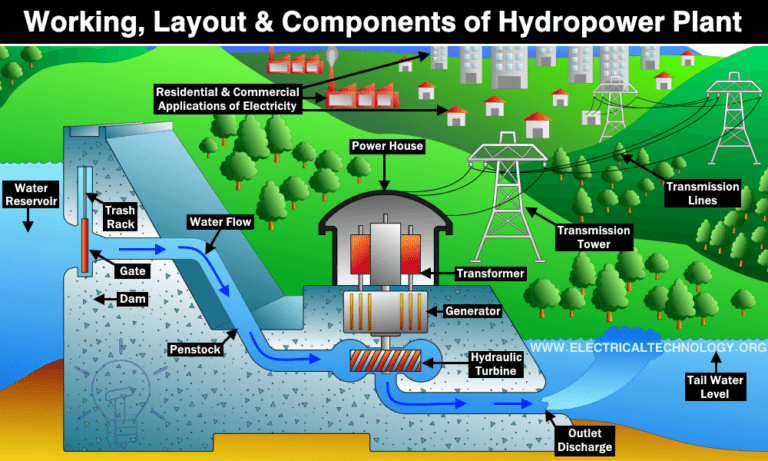
Hydropower, also known as hydro energy, is a renewable energy source that generates electricity by harnessing the power of moving water. Hydropower plants use turbines to convert the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy using a generator.
Hydropower is one of the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy. According to the Department of Energy, hydropower currently accounts for 28.7% of total U.S. renewable electricity generation and about 6.2% of total U.S. electricity generation.
Components of HydroPower Systems
Hydropower systems consist of several components, including:
Dam: A dam is used to create a reservoir of water, which is then released through the turbines to generate electricity.
Intake: The intake is the opening in the dam through which water flows into the power plant.
Penstock: The penstock is a large pipe that carries water from the intake to the turbines.
Turbines: Turbines are used to convert the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy.
Generator: The generator is used to convert the mechanical energy from the turbines into electrical energy.
Transformer: The transformer is used to increase the voltage of the electricity generated by the generator, making it suitable for transmission over long distances.
Hydropower systems can be classified into two types: impoundment and run-of-river.
Impoundment systems use a dam to create a reservoir of water, while run-of-river systems do not use a dam and instead rely on the natural flow of the river to generate electricity.
Hydropower is a clean and renewable energy source that has the potential to play an important role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impacts of building dams and reservoirs, such as habitat destruction and displacement of local communities.
The Role of Hydro Energy in Greentech Solutions
Renewable Energy Source
Hydro energy is a renewable energy source that has been used for centuries. It is generated by the movement of water, and it has become an important part of the Greentech solutions industry. Hydroelectric power plants generate electricity by harnessing the power of falling water. The water is stored in a reservoir, and when it is released, it flows through turbines that generate electricity.
Hydro energy is a clean and renewable energy source that does not emit greenhouse gases. It is a reliable source of energy that can be used to power homes, businesses, and industries. In addition, hydro energy is cost-effective and has a low operating cost. Hydroelectric power plants have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, making them an ideal choice for Greentech solutions.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Hydro energy plays a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint of the energy sector. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the demand for clean energy is increasing. Hydro energy is a clean and renewable energy source that can help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and reduce carbon emissions.
Hydroelectric power plants do not emit greenhouse gases, making them an ideal choice for Greentech solutions. They also help to reduce the reliance on non-renewable energy sources, such as coal and oil. By reducing the carbon footprint of the energy sector, hydro energy is contributing to a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, hydro energy is an important part of the Greentech solutions industry. It is a clean and renewable energy source that can help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and reduce carbon emissions. Hydroelectric power plants are cost-effective, reliable, and have a long lifespan, making them an ideal choice for Greentech solutions.
Benefits of HydroPower
Hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, is a renewable energy source that generates electricity from the energy of falling water. There are several benefits of hydropower, including sustainability, efficiency, and economic advantages.
Sustainability
Hydropower is a sustainable source of energy that produces electricity without emitting harmful greenhouse gases. It is a clean and renewable energy source that does not deplete natural resources. Unlike fossil fuels, hydropower does not produce air pollution or toxic waste. This makes it an environmentally friendly option for generating electricity.
Efficiency
Hydropower is a highly efficient source of energy. It has a high energy conversion rate, which means that a large amount of energy can be generated from a small amount of water. Hydropower plants can also be used to store energy, which makes them a flexible source of energy that can be used to meet peak demand. In addition, hydropower plants have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, which makes them a reliable source of energy.
Economic Advantages
Hydropower is an economically advantageous source of energy. It is a low-cost source of energy that can help reduce electricity bills. Hydropower plants also provide other benefits, such as flood control, irrigation support, and clean drinking water. In addition, hydropower plants can create jobs and stimulate local economies.
Hydropower is a sustainable, efficient, and economically advantageous source of energy. It is a clean and renewable energy source that does not produce harmful emissions or deplete natural resources. Hydropower plants can also provide other benefits, such as flood control, irrigation support, and clean drinking water.
Challenges in HydroPower Implementation
Hydropower is an important source of renewable energy that can contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed in the implementation of hydropower projects.
Environmental Impact
One of the major challenges of hydropower is its potential environmental impact. Building large dams can lead to the displacement of communities and the loss of biodiversity.
The construction of dams can also alter the natural flow of rivers, affecting aquatic ecosystems and fish populations. In addition, the flooding of large areas of land can lead to the release of greenhouse gases from decomposing vegetation.
High Initial Costs
Hydropower projects require significant capital investment, making them challenging to implement in areas with limited financial resources. The construction of dams, turbines, and transmission lines can be expensive, and the costs of maintenance and operation can also be high. In addition, hydropower projects require a long lead time to plan and implement, making them less flexible than other renewable energy sources.
Geographical Limitations
Another challenge of hydropower is its geographical limitations. Hydropower projects require specific geographical features, such as rivers with sufficient flow and elevation changes. This means that not all regions are suitable for hydropower development. In addition, the availability of water can be affected by climate change, leading to reduced power output or even the abandonment of hydropower projects.
Therefore, while hydropower has significant potential as a source of renewable energy, there are several challenges that need to be addressed in its implementation. These challenges include environmental impact, high initial costs, and geographical limitations. By addressing these challenges, it may be possible to increase the contribution of hydropower to the global energy mix and reduce carbon emissions.
Innovations in HydroPower Technology
Hydropower technology has been around for many years, but recent innovations have made it more efficient and environmentally friendly. This section will explore some of the latest advancements in hydropower technology.
Advanced Turbine Designs
One of the most significant innovations in hydropower technology is the development of advanced turbine designs. These turbines are designed to be more efficient and produce more power than traditional turbines. For example, the Kaplan turbine has adjustable blades that allow it to operate at different water flow rates, making it more efficient than traditional turbines.
Another advanced turbine design is the Francis turbine, which is designed to operate at low to medium head heights. This turbine has a curved blade design that allows it to extract more energy from the water and produce more power.
Hydrokinetic Energy
Hydrokinetic energy is another area of innovation in hydropower technology. This technology involves using the kinetic energy of moving water to generate electricity. Hydrokinetic energy systems can be installed in rivers, tidal currents, and ocean currents.
One example of hydrokinetic energy technology is the use of underwater turbines. These turbines are placed in areas of high water flow, such as tidal currents, and use the kinetic energy of the water to generate electricity. Another example is the use of oscillating water columns, which use the movement of waves to generate electricity.
The above innovations in hydropower technology have made it more efficient and environmentally friendly. With continued research and development, hydropower technology has the potential to become a major source of renewable energy in the future.
Case Studies of HydroPower in Greentech Solutions
Norway: Leading in HydroPower
Norway is a country that is well known for its commitment to renewable energy. The country is a leader in hydropower, with over 96% of its electricity generated from hydropower. Norway has a long history of using hydropower, with the first hydropower plant built in 1885. Since then, Norway has continued to invest in the technology, and now has over 1,500 hydropower plants.
Norway's commitment to hydropower has had a significant impact on the country's economy. The industry has created many jobs and has helped to reduce the country's reliance on fossil fuels. In addition, Norway's hydropower plants have helped to keep electricity prices low for consumers.
China: Largest HydroPower Capacity
China is the country with the largest hydropower capacity in the world. The country has invested heavily in hydropower, with over 300 hydropower plants in operation. China's hydropower capacity has increased dramatically in recent years, with a growth rate of over 12% per year between 2000 and 2018.
China's commitment to hydropower has had a significant impact on the country's energy mix. Hydropower now accounts for over 17% of China's electricity generation, making it the second-largest source of electricity in the country after coal. In addition, China's hydropower plants have helped to reduce the country's reliance on fossil fuels, which has had a positive impact on air quality.
Overall, hydropower is an important part of the Greentech solutions for renewable energy. Norway and China are just two examples of countries that have made significant investments in hydropower, and their efforts have paid off in terms of economic growth and energy security.
The Future of HydroPower
Hydropower is one of the oldest and most reliable sources of renewable energy. As the world looks to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, the future of hydropower looks promising. This section will explore the potential growth and emerging markets for hydropower.
Potential Growth
According to a report by Power Technology, hydropower is predicted to grow by 125GW by 2023, despite annual growth having "slowed" in recent years. The report states that the growth is due to the increasing demand for renewable energy sources and the need to reduce carbon emissions.
Hydropower also has the potential to be more efficient and cost-effective than other renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. The International Hydropower Association estimates that hydropower can provide up to 17% of global electricity by 2030.
Emerging Markets
Hydropower has the potential to play a significant role in emerging markets such as Africa and Asia. These regions have vast untapped hydropower potential, and the development of hydropower projects can help to improve access to electricity and support economic growth.
In Africa, the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam is set to become the largest hydropower plant in Africa and will provide electricity to Ethiopia and neighboring countries. In Asia, China is the world's largest producer of hydropower and has ambitious plans to expand its hydropower capacity.
However, it is important to note that the development of hydropower projects must be done in a sustainable and responsible manner. The construction of large dams can have significant environmental and social impacts, and it is crucial to ensure that the benefits of hydropower are balanced with the potential risks.
Overall, the future of hydropower looks promising as the world looks to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. With the potential for significant growth and the ability to support economic development in emerging markets, hydropower is likely to play an important role in the global energy mix.
Conclusion
Hydro energy has proven to be one of the most reliable and cost-effective sources of renewable energy. It is a clean and sustainable source of power that has the potential to meet the world's energy demands without causing harm to the environment.
Hydro energy is an excellent alternative to fossil fuels as it does not produce greenhouse gases or air pollution. It can also help reduce the dependence on foreign oil, which is a significant advantage for countries that rely heavily on oil imports.
Despite its many benefits, hydro energy does have some negative impacts on the environment. Dams can alter the natural flow of rivers, which can affect fish populations and other aquatic life. It can also lead to the displacement of local communities and the loss of cultural heritage sites.
To mitigate these negative impacts, it is essential to ensure that hydro energy projects are designed and implemented with sustainability in mind. This includes conducting proper environmental impact assessments, engaging with local communities, and implementing measures to protect the environment.
In conclusion, hydro energy is a vital part of the transition to a more sustainable future. It is a reliable and cost-effective source of renewable energy that can help reduce the world's dependence on fossil fuels. However, it is essential to balance the benefits of hydro energy with its potential negative impacts on the environment and local communities.
Your Questions Answered
How does hydropower work?
Hydropower is generated by harnessing the power of falling or flowing water. The water is directed through turbines that spin a generator, which produces electricity. The amount of power generated is determined by the speed and volume of the water flow.
What are the advantages of hydropower?
Hydropower is a clean and renewable energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions. It is also highly efficient, with conversion rates of up to 90%. Hydropower plants can be used for both large-scale electricity generation and smaller-scale projects, such as irrigation and water supply.
What are the disadvantages of hydropower?
One of the main disadvantages of hydropower is the potential environmental impact on surrounding ecosystems. Damming rivers can alter the natural flow of water, which can affect fish populations and disrupt habitats. Additionally, large-scale hydropower projects can be expensive to build and maintain.
How does hydropower compare to other forms of renewable energy?
Hydropower is one of the most established forms of renewable energy, and it remains the largest source of renewable electricity generation in the United States. While solar and wind power are growing rapidly, hydropower is still more reliable and consistent, as it is not dependent on weather conditions.
What are some examples of successful hydropower projects?
One of the most well-known hydropower projects is the Hoover Dam, which was completed in 1936 and still generates electricity today. The Three Gorges Dam in China is currently the largest hydropower project in the world, with a capacity of 22.5 GW. In the United States, the Grand Coulee Dam in Washington State is the largest hydropower plant, with a capacity of 6.8 GW.
What is the future of hydropower in the green tech industry?
Hydropower is expected to continue playing an important role in the green tech industry, particularly as countries work to transition to renewable energy sources. While large-scale hydropower projects may face challenges due to environmental concerns, smaller-scale hydropower systems, such as those used for irrigation and water supply, are likely to become more widespread.

